Implantologie, 4/2021
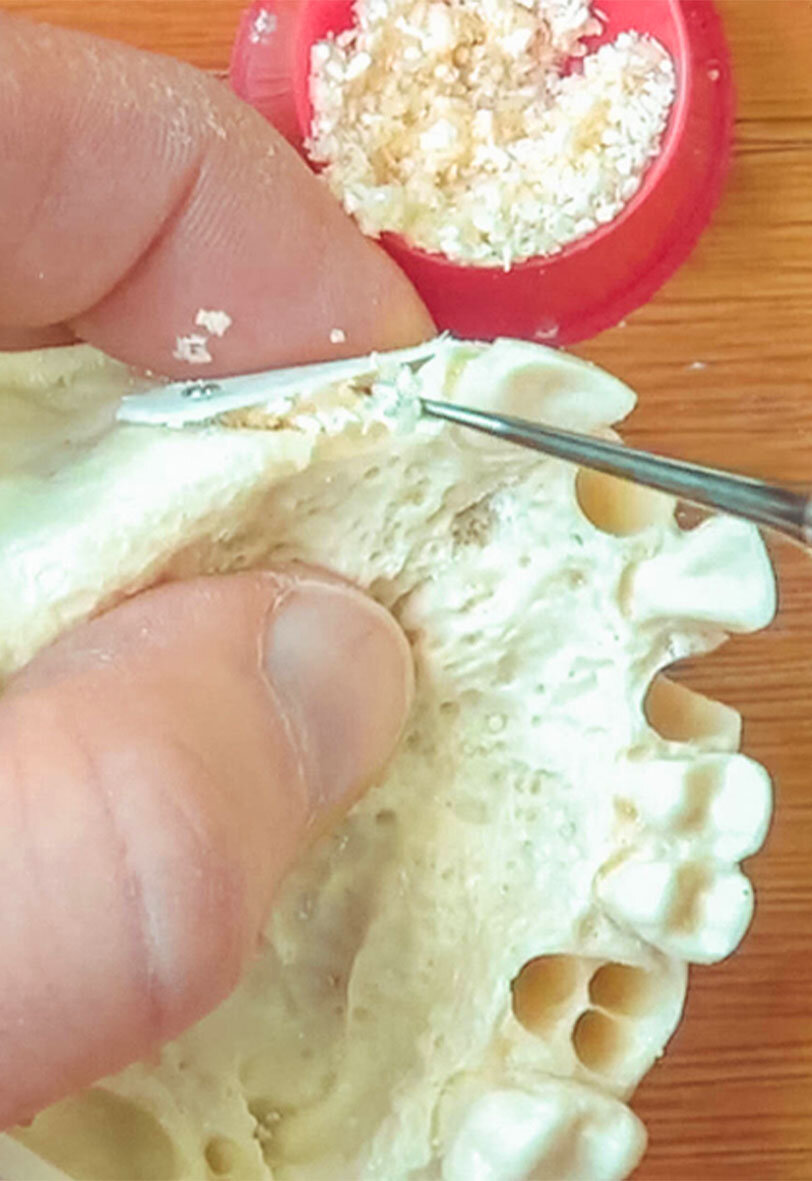
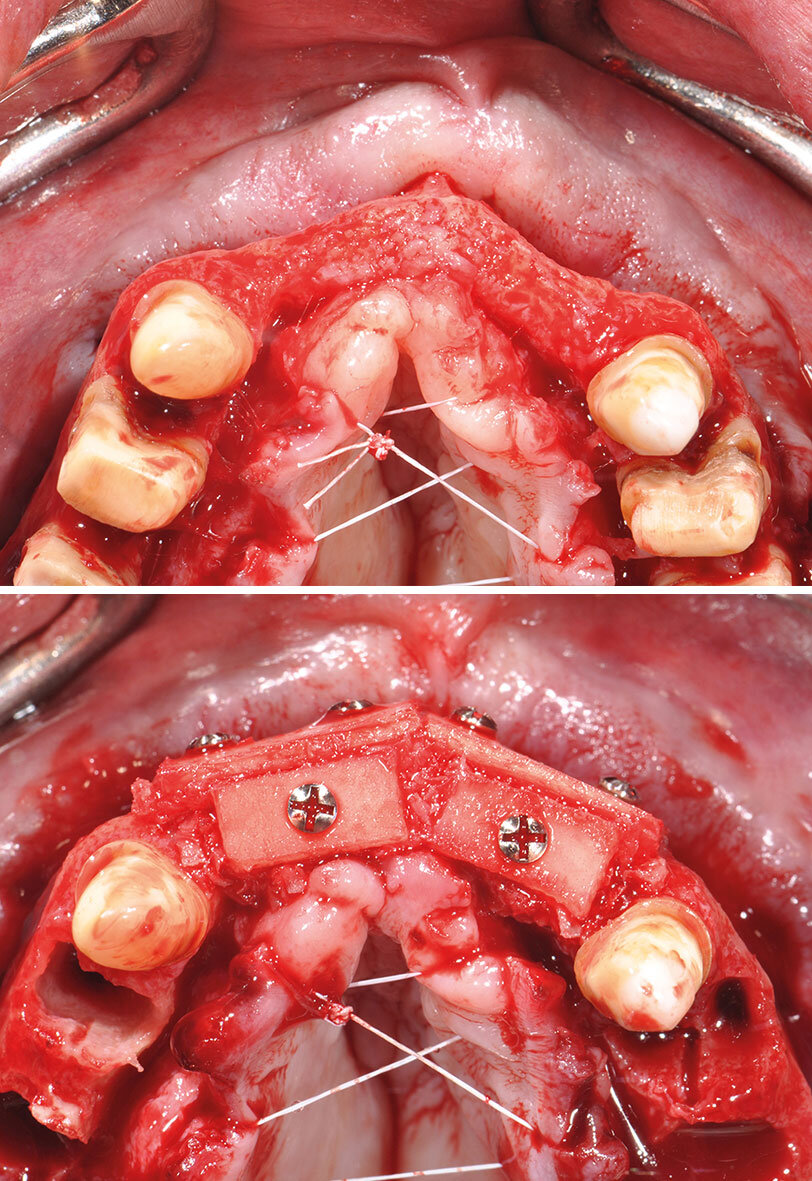
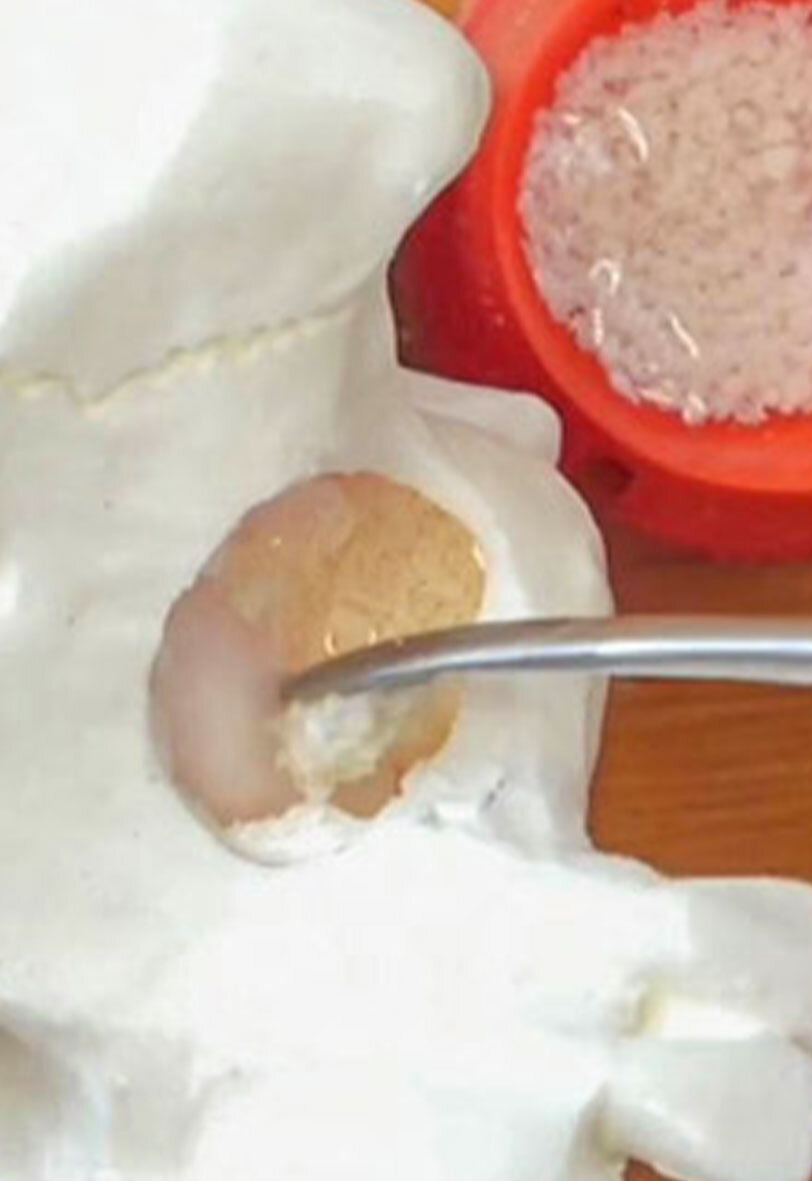
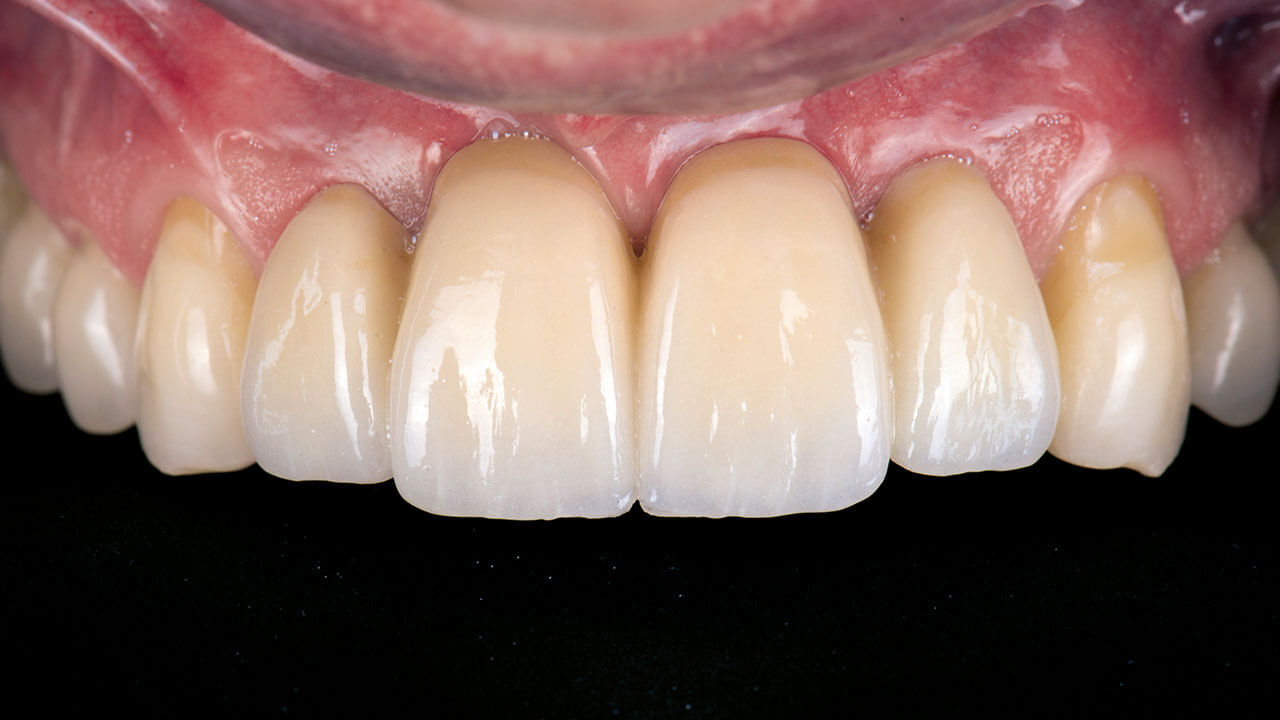
Seiten: 403-412, Sprache: DeutschStelzle, Florian / Kühn, Mathias„Immediate Loading“ und Geweberekonstruktion in einem EingriffDie Sofortimplantation und Sofortbelastung als Ersatz nichterhaltungsfähiger Zähne wird zunehmend zum Standard in der modernen Implantologie. Das Verfahren zeigt unterschiedliche Vorteile für den Patienten und den Gewebeerhalt. Die ausreichende Stabilisierung der Implantate für eine Sofortbelastung ist auch bei reduziertem Restknochen durch aktuelle Techniken und spezielle Implantatdesigns häufig möglich. Als Behandler ist man aber zusätzlich mit meist eingeschränkten Weichgewebeverhältnissen konfrontiert. Will man die Vorteile der Sofortversorgung dennoch nutzen, ist es notwendig, neben dem Wurzel- und Kronenersatz auch das kompromittierte Weichgewebelager zeitgleich zu rekonstruieren und langfristig zu stabilisieren. Der Beitrag stellt anhand eines klinischen Falles die Rekonstruktion von Weich- und Hartgewebe mit zeitgleicher Implantation und Sofortbelastung in einem Eingriff vor. Das Konzept versteht sich als Erweiterung und Kombination klinisch gut validierter Techniken unter Verwendung von xenogenem Augmentationsmaterial.
Manuskripteingang: 14.06.2021, Annahme: 05.10.2021
Schlagwörter: Implantate, Sofortversorgung, Sofortbelastung, xenogene Augmentation, Rekonstruktion, Weichgewebe, Weichgewebeaufbau, Parodontalchirurgie, Knochenersatzmaterial
The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 6/2019
DOI: 10.11607/jomi.7133, PubMed-ID: 31711089Seiten: 1482-1492, Sprache: EnglischRiemann, Max / Wachtel, Hannes / Beuer, Florian / Bolz, Wolfgang / Schuh, Paul / Niedermaier, Robert / Stelzle, FlorianPurpose: Treatment by means of implant-supported immediately loaded fixed full-arch prostheses is known to be related to biologic and technical complications. The aim of this retrospective study was to investigate the prevalence and moment of occurrence of biologic and technical complications happening in immediately loaded fixed full-arch prostheses.
Materials and Methods: This study investigated patients who received treatment with immediately loaded fixed full-arch prostheses using four to six implants from 2007 to 2013. The investigation included biologic and technical complications. Complications were depicted regarding their prevalence and their first time of occurrence. Statistical analysis was performed regarding the differences of the mean complication values between the mandible and the maxilla and between technical and biologic complications.
Results: The investigation included 482 immediately loaded fixed full-arch prostheses (380 patients, mean observation period: 23.5 months). In 193 arches (40%), either technical (30.9%), biologic (6.5%), or both (3.1%) types of complications occurred. Technical complications occurred significantly more often than biologic complications (P .000). The most frequent technical complication was "fracture of veneering material" (24.7%, arch level). The most frequent biologic complication was "marginal bone loss ≥ 2 mm" (16.3%, implant level). The median first advents of technical complications were after 23/26 months (implant-/prosthesisrelated) and after 3 months for biologic complications, respectively. There was no significant difference of the mean complication rates between the maxilla and the mandible (P = .409). In 99.0% of the arches with complications, the restorations could be obtained.
Conclusion: Within this treatment concept, biologic and technical complications may occur over time. However, the vast majority of complications (99.0%) do not affect the overall prosthesis survival. Technical complications are assumed to occur significantly more often than biologic complications. It is suggested that not only stress and material fatigue but also function is a matter concerning this treatment option and, thus, may be a factor related to complication rates.
Schlagwörter: immediate function, immediate implants, immediate loading, immediate placement, implant
Quintessenz Zahnmedizin, 9/2017
ImplantologieSeiten: 1015-1022, Sprache: DeutschSchuh, Paul Leonhard / Bolz, Wolfgang / Riemann, Max / Stelzle, Florian / Beuer, Florian / Wachtel, HannesDie Multi-Layer-Technik - ein evolutionäres KonzeptDie evolutionäre Entwicklung der zahnmedizinischen Behandlung sowie der Materialien und Methoden erlaubt es, unsere Patienten schnell, minimalinvasiv und mit vorhersagbaren Ergebnissen zu versorgen. Etablierte Therapiekonzepte wie die Bone-Lamina-Technik und die Augmentation von subepithelialem Bindegewebe ermöglichen einen neuen Behandlungsansatz. In dem Beitrag wird die Multi-Layer-Technik zur Versorgung von Einzelzahnlücken in der ästhetischen Zone mit Sofortimplantaten in nur einem Eingriff vorgestellt. Bei ersten derart behandelten Patienten konnten stabile Resultate erzielt werden. Daten aus Langzeitstudien sind noch abzuwarten, um den klinischen Erfolg bestätigen zu können.
Schlagwörter: Multi-Layer-Technik, Bone-Lamina-Technik, Augmentation, Sofortimplantation, Ästhetik, Einzelzahnversorgung
The International Journal of Prosthodontics, 5/2017
DOI: 10.11607/ijp.5239, PubMed-ID: 28859180Seiten: 419-425, Sprache: EnglischStelzle, Florian / Riemann, Max / Klein, Alfred / Oetter, Nicolai / Rohde, Maximilian / Maier, Andreas / Eitner, Stephan / Neukam, Friedrich Wilhelm / Knipfer, ChristianAims: Complete maxillary edentulism and prosthetic rehabilitation with removable full dentures are known to affect speech intelligibility. The aim of this study was to prospectively investigate the long-term effect of time on speech intelligibility in patients being rehabilitated with newly fabricated full maxillary dentures.
Materials and Methods: Speech was recorded in a group of 14 patients (male = 9, female = 5; mean age ± standard deviation [SD] = 66.14 ± 7.03 years) five times within a mean period of 4 years (mean ± SD: 47.50 ± 18.16 months; minimum/maximum: 24/68 months) and in a control group of 40 persons with healthy dentition (male = 30, female = 10; mean age ± SD = 59 ± 12 years). All 14 participants had their inadequate removable full maxillary dentures replaced with newly fabricated dentures. Speech intelligibility was measured by means of a polyphone-based speech recognition system that automatically computed the percentage of accurately spoken words (word accuracy [WA]) at five different points in time: 1 week prior to prosthetic maxillary rehabilitation (both with and without inadequate dentures in situ) and at 1 week, 6 months, and a mean of 48 months after the insertion of newly fabricated full maxillary dentures.
Results: Speech intelligibility of the patients significantly improved after 6 months of adaptation to the new removable full maxillary dentures (WA = 66.93% ± 9.21%) compared to inadequate dentures in situ (WA = 60.12% ± 10.48%). After this period, no further significant change in speech intelligibility was observed. After 1 week of adaptation, speech intelligibility of the rehabilitated patients aligned with that of the control group (WA = 69.79% ± 10.60%) and remained at this level during the examination period of 48 months.
Conclusion: The provision of new removable full maxillary dentures can improve speech intelligibility to the level of a healthy control group on a long-term basis.
Implantologie, 4/2015
Seiten: 421-431, Sprache: DeutschStelzle, Florian / Wachtel, Hannes / Bolz, Wolfgang / Niedermaier, Robert / Schuh, Paul Leonhard / Weiß, Michael / Riemann, Max5-Jahres-Fallkohortenstudie der ImplantatüberlebensratenDie Behandlung von Patienten mit zahnlosen und stark atrophierten Kieferkämmen stellt eine anspruchsvolle Herausforderung für die zahnärztliche Praxis dar. Die Versorgung mit Implantaten ist häufig durch kompromittierte und volumenreduzierte knöcherne Verhältnisse erschwert. Durch die Verwendung von 2 axial gesetzten Implantaten in der frontalen und 2 anguliert gesetzten Implantaten in der distalen Region kann das vorhandene Knochenangebot der Prämaxilla im Oberkiefer und interforaminär im Unterkiefer optimal genutzt werden. In dieser Fallkohortenstudie resultiert die Sofortversorgung von 4 primärstabilen Implantaten mit einer festsitzenden Brücke, ausgehend von den Daten bis zu 5 Jahren und 130 Patienten (161 Kiefer, 644 inserierte Implantate), in einer implantären Überlebensrate von 95,4 %. Es zeigten sich weder signifikante Unterschiede zwischen Implantaten, die im Ober- oder Unterkiefer (p = 0,081) inseriert wurden, noch zwischen axial und schräg gesetzten Implantaten (p = 0,202). Das All-on-four-Konzept mit einem Sofortbelastungsprotokoll bietet eine Versorgung, die sicher vorhersagbare Ergebnisse liefert und in nur einem Eingriff erfolgen kann.
Schlagwörter: All-on-four, Implantation, Sofortbelastung, Sofortversorgung
Implantologie, 4/2015
Seiten: 443-451, Sprache: DeutschSchuh, Paul Leonhard / Bolz, Wolfgang / Weiß, Michael / Niedermaier, Robert / Riemann, Max / Stelzle, Florian / Wachtel, HannesSofortimplantation mit simultaner Hart- und Weichgewebeaugmentation in der ästhetischen ZoneDie Einzelzahnversorgung in der ästhetischen Zone der Oberkieferfront mit einem Sofortimplantat erfordert die Kombination etablierter chirurgischer Techniken. Dazu gehören die Weichgewebeaugmentation mit einem subepithelialen Bindegewebe, welches aus der Tuberregion entnommen wird und die Hartgewebeaugmentation mit der Bone-Lamina-Technik. Die Multi-Layer-Technik ermöglicht eine minimalinvasive Versorgung der Einzahnlücke in nur einem Eingriff mit einem Sofortimplantat. Erste Fälle zeigen stabile Ergebnisse. Daten aus Langzeitstudien sind noch abzuwarten, um den klinischen Erfolg bestätigen zu können.
Schlagwörter: Multi-Layer-Technik, Bone-Lamina-Technik, Augmentation, Implantation, GBR, GTR, Sofortimplantation, Ästhetik, Einzelzahn
The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 3/2014
DOI: 10.11607/jomi.3069, PubMed-ID: 24818193Seiten: 550-557, Sprache: EnglischStelzle, Florian / Rohde, MaximilianPurpose: Because the maxilla and its alveolar process are prone to resorption after tooth loss, it is often necessary to perform a bone augmentation procedure to successfully carry out implant treatment in that region. The aim of this study was to determine the adhesive force between the sinus membrane and the osseous sinus floor that occurs during sinus floor elevation with a balloon lift system.
Materials and Methods: Twenty-two ex vivo pig heads were used for this study. Access to the maxillary sinus was gained via the lateral sinus wall. Sinus elevation was performed using an inflatable balloon, which was consecutively filled with 3 mL of a radiopaque fluid. Pressure was monitored directly and continuously during the elevation procedure with an electronic pressure gauge. The integrity of the membrane was checked microscopically and macroscopically.
Results: The average adhesion force of the sinus membrane was found to be 748 ± 65.56 mmHg. On microscopic and macroscopic inspection, no mucosal tearing occurred during sinus floor elevation. Underwood septa, when present, did not significantly influence the adhesion forces.
Conclusions: The balloon system allowed for reproducible real-time measurement of the elevation forces and soft tissue resilience of the sinus membrane during the elevation process in this animal model. No mucosal ruptures were caused with this technical setup, in which effective elevation pressure ranging from 660 to 880 mmHg was not exceeded. A possible transfer of this technical setup to clinical procedures in humans requires investigation.
Schlagwörter: balloon lift, elevation forces, resilience, sinus floor elevation, sinus membrane
The International Journal of Prosthodontics, 1/2014
DOI: 10.11607/ijp.3597, PubMed-ID: 24392479Seiten: 61-69, Sprache: EnglischKnipfer, Christian / Riemann, Max / Bocklet, Tobias / Noeth, Elmar / Schuster, Maria / Sokol, Biljana / Eitner, Stephan / Nkenke, Emeka / Stelzle, FlorianPurpose: Tooth loss and its prosthetic rehabilitation significantly affect speech intelligibility. However, little is known about the influence of speech deficiencies on oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL). The aim of this study was to investigate whether speech intelligibility enhancement through prosthetic rehabilitation significantly influences OHRQoL in patients wearing complete maxillary dentures. Speech intelligibility by means of an automatic speech recognition system (ASR) was prospectively evaluated and compared with subjectively assessed Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP) scores.
Materials and Methods: Speech was recorded in 28 edentulous patients 1 week prior to the fabrication of new complete maxillary dentures and 6 months thereafter. Speech intelligibility was computed based on the word accuracy (WA) by means of an ASR and compared with a matched control group. One week before and 6 months after rehabilitation, patients assessed themselves for OHRQoL.
Results: Speech intelligibility improved significantly after 6 months. Subjects reported a significantly higher OHRQoL after maxillary rehabilitation with complete dentures. No significant correlation was found between the OHIP sum score or its subscales to the WA.
Conclusion: Speech intelligibility enhancement achieved through the fabrication of new complete maxillary dentures might not be in the forefront of the patients' perception of their quality of life. For the improvement of OHRQoL in patients wearing complete maxillary dentures, food intake and mastication as well as freedom from pain play a more prominent role. Int J Prosthodont 2014;27:61-69. doi: 10.11607/ijp.3597
The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 3/2012
PubMed-ID: 22616043Seiten: 513-522, Sprache: EnglischStelzle, Florian / Neukam, Friedrich Wilhelm / Nkenke, EmekaPurpose: Piezoelectric surgery is meant to be a gentle method for implant site preparation (ISP). However, the application of load and its influence on heat development over time and effects on soft tissue are unknown. Therefore, this study sought to evaluate heat development in the bone and the duration of the procedure according to load application, as well as preservation of the sinus floor mucosa during piezoelectric ISP.
Materials and Methods: One hundred twenty implant sites (6 mm deep × 3 mm wide) were prepared in the calvaria of ex vivo pig heads using piezoelectric surgery. The load applied to the working tip was increased in 100-g intervals up to 1,000 g. The bone temperature was measured, and thermal effects were analyzed histomorphometrically. The duration of each ISP was recorded. Another 12 ISPs were performed at the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus in the vicinity of the sinus floor mucosa, and sites were checked for perforation.
Results: Temperature and histologic effects of heat demonstrated a significant positive correlation with the applied load. The duration of ISP was significantly negatively correlated with load application. The maximum temperature generated by piezoelectric surgery was 64.5°C (load of 901 to 1,000 g). At a load of 401 to 500 g, the average temperature was 40.2°C ± 3.3°C, the average thermal damage extended 115.9 ± 16.3 µm beyond the ISP area, and the maximum temperature did not exceed 47°C. The average duration of ISP using this load interval was 45.5 ± 9.4 seconds. Two perforations of the sinus floor mucosa were detected.
Conclusions: In the present setting, the applied load during piezoelectric ISP should not exceed 500 g to prevent temperatures above 47°C in the bony implant socket. With a load of 400 to 500 g, ISP took 40 to 50 seconds.
Schlagwörter: dental implant, implant site preparation, piezosurgery, sinus floor elevation, thermal tissue alteration, time duration
The International Journal of Prosthodontics, 1/2012
PubMed-ID: 22259792Seiten: 24-32, Sprache: EnglischKnipfer, Christian / Bocklet, Tobias / Noeth, Elmar / Schuster, Maria / Sokol, Biljana / Eitner, Stephan / Nkenke, Emeka / Stelzle, FlorianPurpose: A completely edentulous or partially edentulous maxilla involving missing anterior teeth may impact speech production and lead to reduced speech intelligibility. The aim of this study was to prospectively evaluate the effect of a dental prosthetic rehabilitation on speech intelligibility in patients with a toothless or interrupted maxillary arch by means of an automatic, standardized speech recognition system.
Materials and Methods: The speech intelligibility of 45 patients with complete tooth loss or a loss including missing anterior teeth in the maxilla was evaluated by means of a polyphone-based automatic speech recognition system that assessed the percentage of correctly recognized words (word accuracy). To replace inadequate maxillary removable dentures, 20 patients from the overall sample had been rehabilitated with complete dentures and 25 patients with telescopic prostheses. Speech recordings were made in four recording sessions (with and without existing prostheses and then at 1 week and 6 months after placement of newly fabricated prostheses).
Results: Significantly higher speech intelligibility was observed in both patient groups compared to the original results without the dentures inserted. After 6 months of adaptation, both groups had reached a level of speech quality that was comparable to the healthy control group. However, patients receiving new telescopic prostheses showed significantly higher levels of speech intelligibility compared to those receiving new complete dentures. Within 6 months, speech intelligibility did not significantly improve from the level found 1 week after insertion of new prostheses for both groups.
Conclusion: Patients benefit from the fabrication of new dentures in terms of speech intelligibility, regardless of the type of prosthesis. However, telescopic crown prostheses yield significantly better speech quality compared to complete dentures.