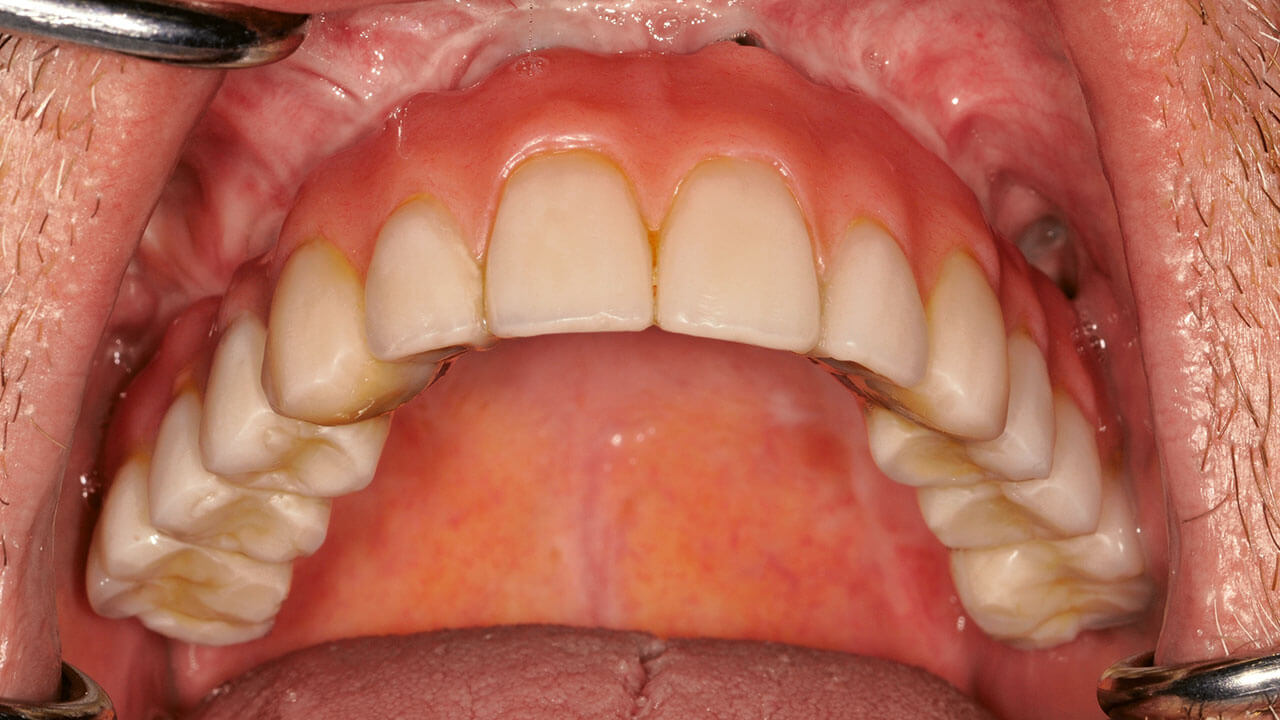
Implantologie, 3/2022
Páginas 291-300, Idioma: AlemánGülses, Aydin / Behrens, Eleonore / Aktas, Oral Cenk / Acil, Yahya / Wiltfang, JörgChirurgische Prinzipien und materialwissenschaftliche AspekteEinteilige provisorische Implantate sind Hilfselemente, die grundsätzlich zur Fixation von festsitzendem und herausnehmbarem provisorischem Zahnersatz designt und hergestellt werden. Dieses Therapieverfahren ist gerade für eine anspruchsvolle Patientenklientel von besonderem Interesse, da trotz der Etablierung der neuen Konzepte eine prothetische Sofortversorgung nicht immer durchzuführen ist. Dank der materialwissenschaftlichen Entwicklungen können definitive Ergebnisse auch von provisorischen Implantaten erwartet werden. Dabei sollte aber nicht vergessen werden, dass das übergeordnete Behandlungsziel von provisorischen Implantaten nicht die Osseointegration ist, sondern hier die Funktion als Hilfselement zu einer provisorischen Versorgung vorrangig ist.
Manuskripteingang: 14.06.2022, Annahme: 20.08.2022
Palabras clave: Miniimplantate, provisorisch, Osseointegration, Titan
International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 4/2017
DOI: 10.11607/prd.2238, ID de PubMed (PMID): 28609493Páginas 490-497, Idioma: InglésSencimen, Metin / Gulses, Aydin / Varol, Altan / Ayna, Mustafa / Ozen, Jülide / Dogan, Necdet / Açil, YahyaThe aim of this study was to present the use of retroauricular full-thickness skin grafts in vestibuloplasty surgeries for dental implant rehabilitation in vascularized fibula grafts. Two patients underwent mandibular reconstruction with vascularized fibula grafts due to mandibular gunshot injuries. Inadequate sulcus gaps secondary to mandibular soft tissue deficiencies were managed by full-thickness autologous skin grafts harvested from the retroauricular region. Dental rehabilitation was achieved by implants placed in free fibula grafts. In both cases, complete graft survival was achieved. Cosmetic and functional outcomes were satisfactory. Owing to its high resiliency and elasticity and its thin and hairless structure, full-thickness retroauricular skin graft is an effective treatment modality in the management of intraoral soft tissue deficiencies. Patients with gunshot injuries present great functional and esthetic demands, and every report presenting new treatment modalities is helpful in the management of the condition.
International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 5/2016
DOI: 10.11607/prd.2562, ID de PubMed (PMID): 27560678Páginas 730-735, Idioma: InglésGülses, Aydin / Ayna, Mustafa / Güçlü, Hakan / Sencimen, Metin / Basiry, M. Nabi / Gierloff, Matthias / Açil, YahyaThe aim of this study was to analyze the primary stability of BoneTrust Sinus implants (BTSIs), which are intended to enable higher primary stability by their special design with reduced thread section in cases of reduced vertical bone availability, in comparison with standard BoneTrust implants (SBTIs) in vitro. A bone window 3 cm in length, 4 cm in width, and 3 cm in depth, resembling the maxillary bone window of the lateral sinus wall with 4 mm of residual bone height, was prepared at the dorsal side of freshly slaughtered bovine ribs. One single BTSI and a single SBTI with the same diameter (4 or 5 mm) were placed in each window. After implant placement, the implant stability quotient (ISQ) was measured by using resonance frequency analysis with an Osstell device. A total of 88 implants were placed. ISQ values varied between 63 and 84. Among the implants with 4-mm diameter, all BTSIs showed higher ISQ values compared with SBTIs. One-way analysis of variance showed a significant difference between BTSIs/SBTIs (P .05). BTSIs with 4-mm diameter showed statistically higher values compared to BTSIs with 5-mm diameter (P .05). Among the implants with 5-mm diameter, all SBTIs showed higher ISQ values compared to BTSIs but there was no significant difference. The use of 4-mm-diameter BTSIs could present higher ISQ values during simultaneous implant placement in conjunction with lateral sinus floor augmentation.
International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 4/2015
DOI: 10.11607/prd.2135, ID de PubMed (PMID): 26133144Páginas 540-547, Idioma: InglésAyna, Mustafa / Açil, Yahya / Gulses, AydinThis report assesses the results following sinus floor augmentation performed 14 years previously in which bovine bone xenograft material was used without implant insertion. After sinus floor augmentation, using a 20:80 mixture of autogenous bone and inorganic bovine bone material (Bio-Oss), bone biopsy specimens were taken from the grafted site, processed with Donath's sawing and grinding technique, stained with toluidine blue, and mounted on high-sensitivity plates for histology and microradiography. Histologic and microradiographic analysis showed the ingrowth of newly formed bone into the graft with interspersed residual Bio-Oss granules. The percentage of Bio- Oss and newly formed bone was 10.18% and 9.32%, respectively, within a total surface area of 70.61 mm2 at the site of the corresponding missing first molar, and the percentage of Bio-Oss and newly formed bone was 11.47% and 14.96%, respectively, within a total surface area of 63.92 mm2 at the corresponding missing second molar. The newly formed bone was vital without signs of resorption. This study produced strong evidence that newly formed bone was distributed throughout the bone substitute material around all of its granules and that the grafted site consisted of vital bone even in its central parts. The differences in degradation rate and/or whether the effect of bone graft substitutes alone and/ or in combination with other types, shapes, and sizes of graft materials needs further clinical investigation, especially in regard to long-term changes.
Quintessence International, 9/2013
DOI: 10.3290/j.qi.a29185, ID de PubMed (PMID): 23479589Páginas 689-697, Idioma: InglésBayar, Gurkan Rasit / Yildiz, Selda / Gulses, Aydin / Sencimen, Metin / Acikel, Cengiz Han / Comert, AyhanObjectives: The residual alveolar bone height at the implant recipient site plays a key role in determination of the risk of sinus membrane perforation during crestal sinus elevation. In this study, we aimed to determine the correlation between residual ridge height and perforation limit of sinus membrane and to examine the safety range for the sinus membrane continuity in crestal sinus elevation. Formalin-fixed cadavers were used for the experiment to observe outcomes.
Method and Materials: Crestal sinus elevations were performed on 14 preserved human cadavers' heads. Residual ridge heights were measured using a bone caliper. The physiodispenser was preset to 30 Ncm and sinus floors were elevated by a concave sinus screw with diameter of 4 mm until sinus membrane perforation occurred. The perforations were identified either as Class I or Class II and the portion of the concave sinus screw in the sinus was measured each time using a ruler. Spearman's correlation coefficient was calculated to show the relation between the residual ridge heights and the membrane elevations at the time of perforation of the sinus membranes.
Results: In general, the perforation limit of sinus membrane after elevation was higher with greater residual ridge height. A statistically significant correlation was found between residual ridge heights and perforations of the sinus membrane (r = 0.620, P .001).
Conclusion: Although it is not always possible to extrapolate results from cadavers to an in vitro clinical setting, it could be considered to have clinical significance. Our findings suggest that higher subsinusoidal elevation may be achieved when the residual ridge bone height increases. The conclusions of this study should be verified with studies of more rigorous design.
Palabras clave: crestal approach, perforation, sinus lift
Quintessence International, 10/2012
ID de PubMed (PMID): 23115765Páginas 863-870, Idioma: InglésAydintug, Yavuz Sinan / Bayar, Gürkan Rasit / Gulses, Aydin / Misir, Ahmet Ferhat / Ogretir, Ozlem / Dogan, Necdet / Sencimen, Metin / Acikel, Cengiz HanObjective: When a mandibular third molar is partially impacted in the soft tissue, it must be determined whether the extraction wound should be left partially open or completely closed. We hypothesize that a blood clot preserving a surgical wound with easily cleanable surfaces by primary closure and drain application would postoperatively minimize dry socket and/or alveolitis development.
Method and Materials: Twenty patients requiring bilateral extraction of partially soft tissue-impacted mandibular third molars in a vertical position were included in the study. The existence of dry sockets, alveolitis, pain, facial swelling, and trismus were evaluated on the second, fifth, and seventh days of the postoperative period.
Results: On the second day, pain, trismus, and swelling were higher in the drained group; however, pain reduced progressively in the drained group over time. There were no cases of dry sockets or alveolitis except for a single patient on the seventh day in the drained group over the 7-day study period. On the other hand, in the secondary closure group, the number of dry sockets was 8 (40%) on the second day. The number of alveolitis was 10 (50%) on the fifth day and 4 (20%) on the seventh day.
Conclusion: Closed healing by drain insertion after removal of partially soft tissue-impacted third molars produces less frequent postoperative dry sockets and/ or alveolitis development than occurs with open healing of the surgical wound. In cases with a risk of alveolitis development (lack of oral hygiene, immunocompromised patients, etc), it can be avoided with the "kiddle effect" and related undesired complications by implementing closed healing with drain insertion.
Palabras clave: alveolitis, closed healing, drain insertion, third molar
The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 1/2011
Sólo en líneaID de PubMed (PMID): 21365033Páginas 203, Idioma: InglésSençimen, Metin / Delilbasi, Cagri / Gülses, Aydin / Okçu, Kemal Murat / Gunhan, Omer / Varol, AltanFocal osteoporotic bone marrow defects usually appear as asymptomatic radioluencies in the edentulous posterior mandible of middle-aged women. The exact causative factor in the majority of focal osteoporotic bone marrow defects is still unknown. Because of their radiological similarity with many intraosseous lesions, accurate diagnosis is possible only with histopathological examination. A focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect that occurred 2 years postoperatively apical to an implant is presented with clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic features. According to the literature scan, this is the first case report of this phenomenon caused by a dental implant.
Palabras clave: bone marrow, defect, dental implant, hematopoietic, hemoglobin h
Quintessence International, 9/2010
ID de PubMed (PMID): 20806096Páginas 725-729, Idioma: InglésSabuncuoglu, Fidan Alakus / Sencimen, Metin / Gülses, AydinA 16-year-old girl was referred for surgical-orthodontic treatment with the chief complaint of an unerupted mandibular left second molar. With the exception of this molar, the patient had a fully erupted permanent dentition. A panoramic radiograph showed a horizontally impacted mandibular left second molar beneath a mesially impacted third molar. A surgical approach was used to upright and reposition the impacted second molar. When a molar is severely impacted, surgical uprighting may provide a viable option when other treatment modalities are contraindicated. This case shows an example of successful use of a surgical approach for uprighting and repositioning an impacted molar. The impacted molar was moved into its proper position with surgical exposure, after which it showed good stability.
Palabras clave: impaction, mandibular second molar, molar repositioning
Quintessence International, 4/2010
ID de PubMed (PMID): 20305863Páginas 295-297, Idioma: InglésSencimen, Metin / Gulses, Aydin / Ogretir, Ozlem / Gunhan, Omer / Ozkaynak, Ozkan / Okcu, Kemal MuratCalcium salt deposits in the presence of normal calcium/phosphorus metabolism involving tissues that do not physiologically calcify are referred to as dystrophic calcification. The condition may be associated with a variety of systemic disorders. Additionally, injured tissue of any kind is predisposed to dystrophic calcification. The case of a 21-year-old man with two isolated dystrophic calcifications in the right masseter muscle is presented. Dystrophic calcifications should be studied carefully and differentiated from lesions resulting from other syndromes that manifest calcification of soft tissues. The lack of a classification system of soft tissue calcifications complicates the management and study of the condition.
Palabras clave: calcification, choristoma, dystrophy, masseter muscle