International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, 3/2021
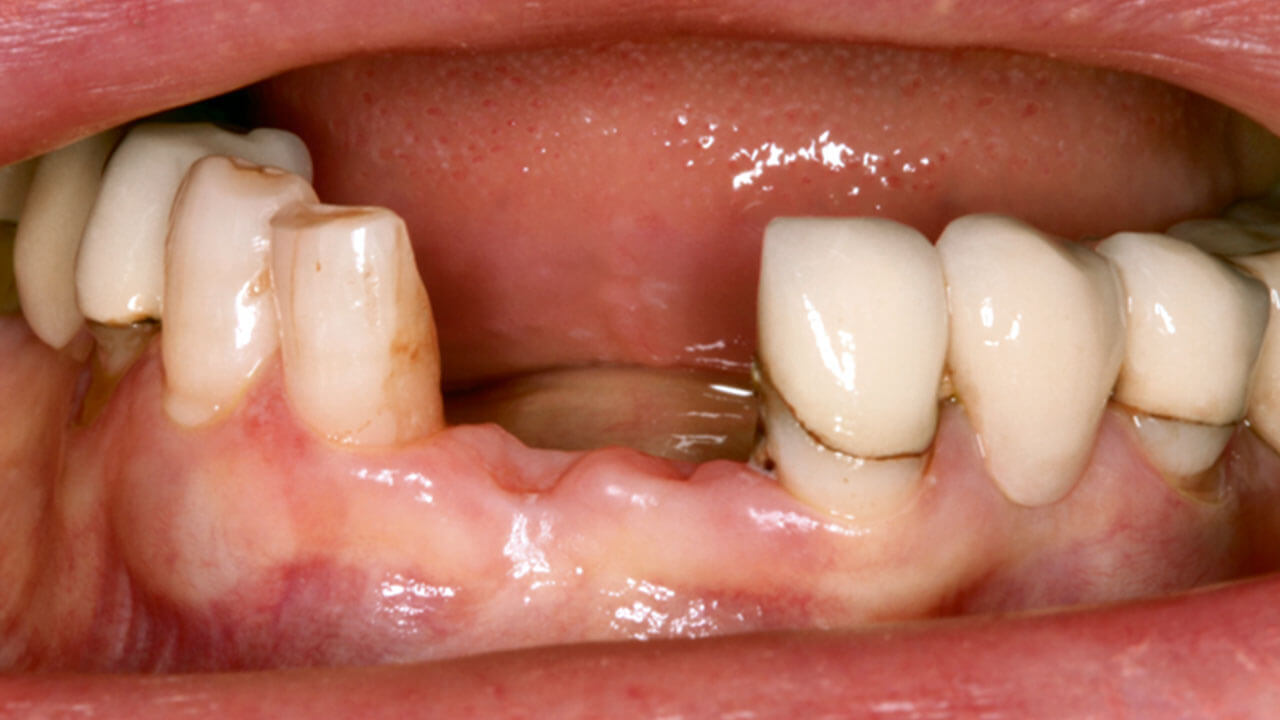
ScienceID de PubMed (PMID): 34553891Páginas 263-273, Idioma: Inglés, AlemánSchnutenhaus, Sigmar / Edelmann, Cornelia / Knipper, Anne / Schöne, André / Luthardt, RalphAim: One-piece ceramic implants (O-PCIs) have proven to be clinically useful, with high survival rates. The biocompatibility and bio-inert characteristics of ceramics in addition to the fact that minimal plaque deposits occur on these materials provide esthetic advantages and justification for their use in the anterior maxilla. The objective of the present study was to investigate the suitability of O-PCI use in the anterior maxilla.
Materials and methods: The data of patients who had received conventional two-piece titanium implants were analyzed. Virtual planning was performed to determine whether O-PCIs could have been used. Three groups were formed: single-tooth gap (group A); multiple-tooth gap treated with two implants (group B); and complex treatments with at least three implants (group C). In addition to assessing the feasibility of O-PCIs, their usefulness as well as additional procedures such as augmentation and a change in the implant quantity or position were evaluated. Values of the location of the virtual cementation line were summarized for all cases.
Results: Without additional procedures, O-PCIs could be used in 97.9% of group A, 77.3% of group B, and 59.1% of group C. For group B, 18.2% of the cases could have been managed with additional augmentation. For the complex cases (group C), 18.2% of the patients would have been treatable if the planning had been altered, augmentation had been performed or implants with an inclined abutment had been available. The mean value of the lowest point of the cementation line was 2.9 mm (standard deviation 1.23; 0.0 to 7.2 mm).
Conclusion: O-PCIs can be used in the anterior maxilla with planning. The esthetic advantages of ceramics can be leveraged for this part of the mouth, especially for single-tooth gaps.
Palabras clave: dental implant, maxillary, one-piece implant, zirconia, ceramic implant, digital treatment simulation
Implantologie, 3/2021
Páginas 315-325, Idioma: AlemánEdelmann, Cornelia / Wetzel, Martin / Schnutenhaus, SigmarÜbersicht und KasuistikDentale Implantate können anhand von dreidimensionalen Daten der Hart- und Weichgewebe vor dem chirurgischen Eingriff virtuell hinsichtlich einer prothetisch optimalen Lage geplant werden. Durch dynamische Navigationsverfahren wird deren Position anschließend auf die klinische Situation am Patienten übertragen. Zu den Vorteilen der dynamischen Navigation gegenüber der schablonengeführten Navigation zählen die Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Implantatsystemen, die Unabhängigkeit von speziellen Bohrsystemen, das Implantieren unter Sicht, die Möglichkeit, intraoperative Änderungen unkompliziert vornehmen zu können, und die erleichterte Navigation in distalen Arealen. Die Ergebnisse der computergestützten dynamischen Navigation sind mit den Ergebnissen der statischen Navigation vergleichbar. Mindestabstände zu gefährdeten anatomischen Strukturen sind bei allen Verfahren der geführten Implantatinsertion einzuhalten. Eine ausgeprägte Lernkurve und das Vermeiden möglicher Fehlerquellen bei der Datenerhebung und bei der Übertragung der Implantatposition, wie zum Beispiel Patientenbewegungen, inkorrekte Positionierung der Referenzmarker oder fehlerhafte Zuordnung der Referenzmarker im Implantatplanungsprogramm, sind zu beachten. In diesem Beitrag werden die theoretischen Aspekte der dynamischen Navigation und die klinische Anwendung anhand von zwei Behandlungsfällen eingehend beleuchtet.
Manuskripteingang: 16.05.2021, Annahme: 22.08.2021
Palabras clave: computerassistierte Chirurgie, dynamische Navigation, Echtzeit-Navigation, dentale Implantate
Implantologie, 1/2020
Páginas 25-36, Idioma: AlemánSchnutenhaus, Sigmar / Buschbeck, Eric / Luthardt, Ralph G. / Edelmann, CorneliaZu den Vorteilen einer Sofortimplantation zählen eine reduzierte Gesamtbehandlungszeit und in Kombination mit der Sofortbelastung die unmittelbare Eingliederung eines befestigten Provisoriums. Das Erreichen der notwendigen Primärstabilität in der optimalen Implantatposition und das Weichgewebemanagement stellen besondere Herausforderungen dar. Die Überlebensraten einer Sofortimplantation sind vergleichbar mit den Ergebnissen einer verzögerten oder späten Implantation. Ebenso stellen die Sofortbelastung und die konventionelle Belastung gleichermaßen erfolgreiche Belastungsprotokolle dar. Das Beachten der Risikofaktoren sowie eine sorgfältige Patientenselektion sind besonders für das ästhetische Ergebnis von Bedeutung, da es bei Sofortimplantationen zu Rezessionen kommen kann, die dann nicht mehr korrigierbar sind. Eine simultane Alveolar-Ridge- Preservation wirkt sich positiv auf Hart- und Weichgewebe aus und wird empfohlen. Neben der korrekten Einschätzung der morphologischen und patientenindividuellen Risiken gilt es, zusätzlich ein geeignetes Implantatsystem zu wählen. In diesem Beitrag werden klinische Aspekte der Sofortimplantation in der Theorie und anhand von drei Behandlungsfällen umfassend beleuchtet.
Manuskripteingang: 26.07.2019; Annahme: 08.10.2019
Palabras clave: Sofortimplantation, Belastungsprotokoll, Sofortbelastung, Alveolar-Ridge-Preservation, Rezession, Weichgewebemanagement